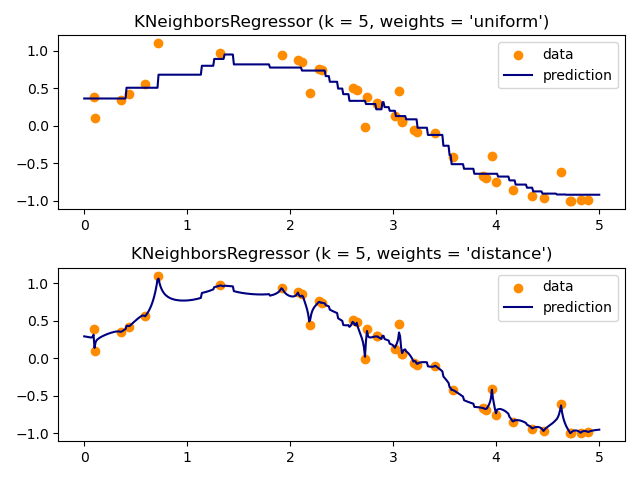
最近鄰回歸?
本案例展示了使用k近鄰的回歸問題的解決方案,以及使用重心和恒定權重對目標進行插值方法。
輸入:
print(__doc__)
# 作者: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# Fabian Pedregosa <fabian.pedregosa@inria.fr>
#
# 執照: BSD 3 clause (C) INRIA
# #############################################################################
# 獲得樣本數據
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import neighbors
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.sort(5 * np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0)
T = np.linspace(0, 5, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
# 在標簽中添加噪音
y[::5] += 1 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(8))
# #############################################################################
# 擬合回歸模型
n_neighbors = 5
for i, weights in enumerate(['uniform', 'distance']):
knn = neighbors.KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors, weights=weights)
y_ = knn.fit(X, y).predict(T)
plt.subplot(2, 1, i + 1)
plt.scatter(X, y, color='darkorange', label='data')
plt.plot(T, y_, color='navy', label='prediction')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.legend()
plt.title("KNeighborsRegressor (k = %i, weights = '%s')" % (n_neighbors,
weights))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
腳本的總運行時間:0分0.173秒。
輸出: