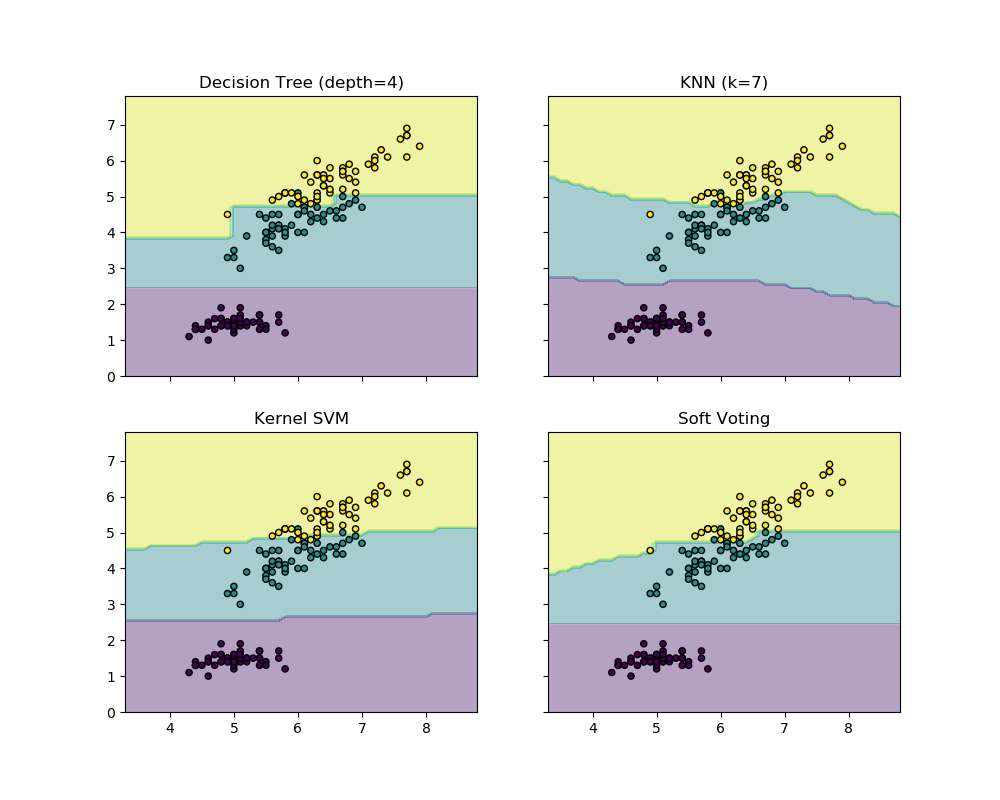
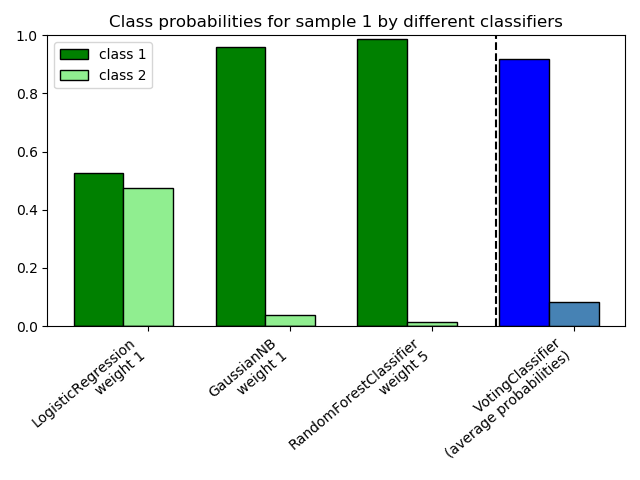
sklearn.ensemble.VotingClassifier?
class sklearn.ensemble.VotingClassifier(estimators, *, voting='hard', weights=None, n_jobs=None, flatten_transform=True, verbose=False)
針對非擬合估計器的Soft Voting/Majority規則分類器。
0.17新增功能。
在用戶指南中閱讀更多內容。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| estimators | list of (str, estimator) tuples 在投票分類器上調用 fit方法將你和存儲在類屬性self.estimators_中的原始估計器的克隆體。可以使用set_params將評估器設置為“drop”。- 版本0.21中的更改:“drop”收錄進該版本。 自版本0.22以來已棄用: 使用None刪除評估器在0.22中已棄用,在0.24中刪除了該功能并使用字符串'drop'代替。 |
| voting | {‘hard’, ‘soft’}, default=’hard’ 如果是"hard",則使用預測的類標簽進行多數決定投票。如果“soft”,預測類標簽基于預測概率總和的最大值,這是一個精心校準的分類器的集成推薦。 |
| weights | array-like of shape (n_classifiers,), default=None 權重序列( float或int),用于在平均(soft voting)之前對預測的類標簽(hard voting)或類概率的出現進行加權。如果沒有,使用統一的權重。 |
| n_jobs | int, default=None int, default=None 所有并行 estimators fit作業數量。除非在joblib.parallel_backend中,否則None表示是1。-1表示使用所有處理器。參見Glossary了解更多細節。0.18版本新功能 |
| flatten_transform | bool, default=True 如果 voting= 'soft'且flatten_transform=True, 轉化方法返回大小為(n_samples, n_classifiers * n_classes)的矩陣。如果flat _transform=False,它返回(n_classifiers, n_samples, n_classes)。 |
| verbose | bool, default=False 如果為True,擬合時經過的時間將在擬合完成時打印出來。 |
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| estimators_ | list of estimators 估計器參數的元素,已在訓練數據上擬合。如果一個估計器被設置為“drop”,那么它將不會出現在 estimators_中。 |
| named_estimators_ | Bunch屬性來按名稱訪問任何擬合的子估計器。 |
| classes_ | array-like of shape (n_predictions,) 類標簽。 |
另見
VotingRegressor預測投票回歸量。
實例
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
>>> from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
>>> from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, VotingClassifier
>>> clf1 = LogisticRegression(multi_class='multinomial', random_state=1)
>>> clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=1)
>>> clf3 = GaussianNB()
>>> X = np.array([[-1, -1], [-2, -1], [-3, -2], [1, 1], [2, 1], [3, 2]])
>>> y = np.array([1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2])
>>> eclf1 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[
... ('lr', clf1), ('rf', clf2), ('gnb', clf3)], voting='hard')
>>> eclf1 = eclf1.fit(X, y)
>>> print(eclf1.predict(X))
[1 1 1 2 2 2]
>>> np.array_equal(eclf1.named_estimators_.lr.predict(X),
... eclf1.named_estimators_['lr'].predict(X))
True
>>> eclf2 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[
... ('lr', clf1), ('rf', clf2), ('gnb', clf3)],
... voting='soft')
>>> eclf2 = eclf2.fit(X, y)
>>> print(eclf2.predict(X))
[1 1 1 2 2 2]
>>> eclf3 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[
... ('lr', clf1), ('rf', clf2), ('gnb', clf3)],
... voting='soft', weights=[2,1,1],
... flatten_transform=True)
>>> eclf3 = eclf3.fit(X, y)
>>> print(eclf3.predict(X))
[1 1 1 2 2 2]
>>> print(eclf3.transform(X).shape)
(6, 6)
方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
fit(X[, y, sample_weight]) |
擬合估計器。 |
fit_transform(X[, y]) |
擬合估計器和變換數據集。 |
get_params([deep]) |
從集成中得到估計器的參數。 |
predict(X) |
預測X的類標簽。 |
score(X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回給定測試數據和標簽的平均精度。 |
set_params(**params) |
從集成中設置估計器的參數。 |
transform(X) |
返回每個估計器X的類標簽或概率。 |
__init__(estimators, *, voting='hard', weights=None, n_jobs=None, flatten_transform=True, verbose=False)
初始化self。有關準確的簽名,請參見help(type(self))。
fit(X, y, sample_weight = None)
擬合估計器。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 訓練向量,其中n_samples為樣本數量,n_features為特征數量。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 目標值。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 樣本權重。如果沒有,那么樣本的權重相等。注意,只有當所有的潛在估計器都支持樣本權值時,才支持此方法。 0.18新增功能 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| self | object |
fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)
擬合數據,然后轉換它。
使用可選參數fit_params將transformer與X和y匹配,并返回X的轉換版本。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 訓練向量,其中n_samples為樣本數量,n_features為特征數量。 |
| y | ndarray of shape (n_samples,), default=None 目標值。 |
| **fit_params | dict 其他擬合參數。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X_new | ndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new) 轉化后的數組。 |
get_params(deep=True)
從集成中得到估計器的參數。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| deep | deep : bool, default = True 將其設置為True將獲得各種分類器以及分類器的參數。 |
predict(X)
預測X的分類。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 輸入樣本。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| maj | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 預測后的分類標簽。 |
property predict_proba
計算X中樣本可能結果的概率。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 輸入樣本。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| avg | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 加權平均每類每個樣本的概率 |
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)
返回給定測試數據和標簽的平均精度。
在多標簽分類中,這是子集精度,同時也是個苛刻的指標,因為你需要對每個樣本正確預測每個標簽集。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 測試樣本。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)X的正確標簽。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 樣本權重。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| score | float self.predict(X) 關于y的平均準確率。 |
set_params(**params)
從集成中設置估計器的參數。
有效的參數鍵可以用get_params()列出。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| **params | keyword arguments 使用例如 set_params(parameter_name=new_value)的特定參數。此外,為了設置堆料估算器的參數,還可以設置疊加估算器的單個估算器,或者通過將它們設置為“drop”來刪除它們。 |
transform(X)
返回每個估計量X的類標簽或概率。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 訓練向量,其中 n_samples為樣本數量,n_features為特征數量。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| probabilities_or_labels | If voting='soft' and flatten_transform=True:返回大小為 (n_classifiers, n_samples * n_classes)的ndarray,為每個分類器計算的類概率。If voting='soft' and flatten_transform=False:返回大小為 (n_classifiers, n_samples, n_classes)的ndarray。If voting='hard':返回大小為 (n_samples, n_classifiers)的ndarray,是每個分類器預測的類標簽。 |