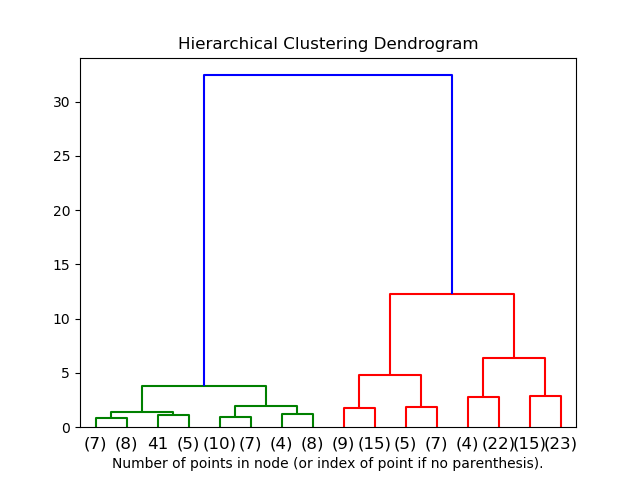
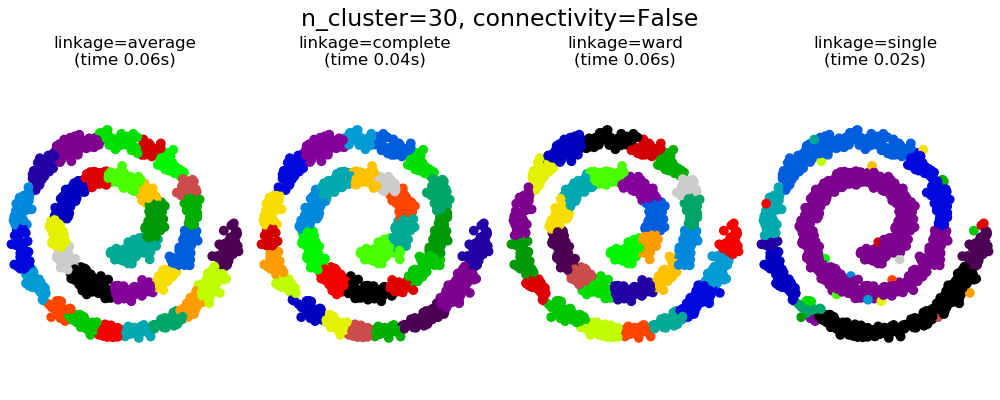
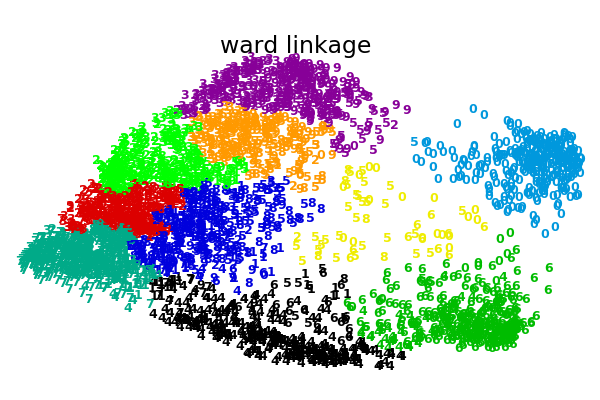
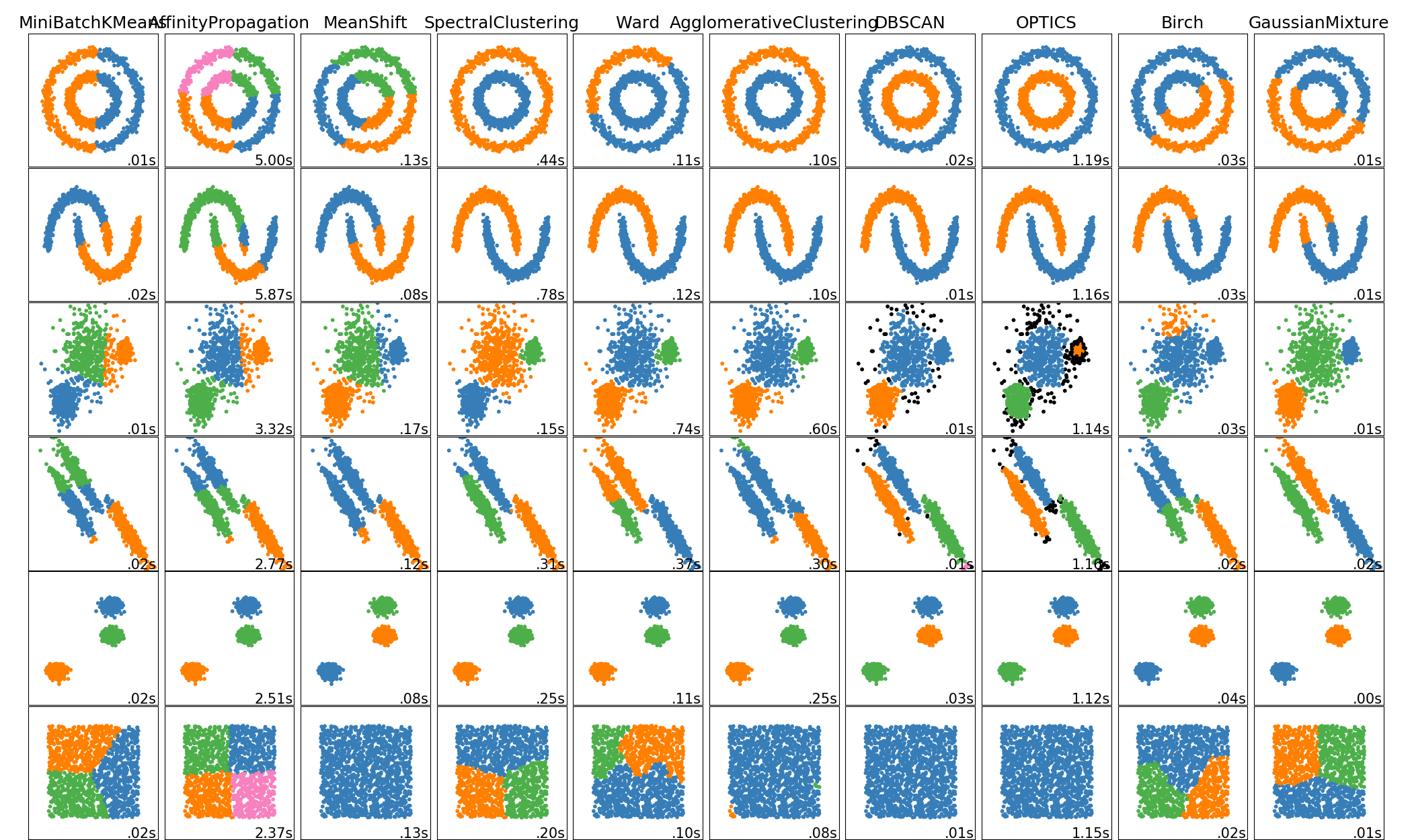
sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering?
class sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2, *, affinity='euclidean', memory=None, connectivity=None, compute_full_tree='auto', linkage='ward', distance_threshold=None)
凝聚聚類
遞歸地合并成對聚類,以最小的方式增加給定的鏈接距離。
在用戶指南中閱讀更多內容。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| n_clusters | int or None, default=2 要查找的聚類數目。如果 distance_threshold 不是None, 它就必須是None。 |
| affinity | str or callable, default=’euclidean’ 用于計算連接的度量。可以是“euclidean”, “l1”, “l2”, “manhattan”, “cosine”, 或者“precomputed”。如果linkage是“ward”, 只有“euclidean”是被接受的。 如果“precomputed”,則需要一個距離矩陣(而不是相似矩陣)作為擬合方法的輸入。 |
| memory | str or object with the joblib.Memory interface, default=None 用于儲存樹計算的輸出。默認情況下,不執行緩存。如果給出一個字符串,它就是緩存目錄的路徑。 |
| connectivity | array-like or callable, default=None 連接矩陣。為每個樣本定義遵循給定數據結構的相鄰樣本。這可以是連接矩陣本身,也可以是可調用的,能將數據轉換為連接矩陣,例如從kneighbors_graph派生的連接矩陣。默認為None,分層聚類算法是一種非結構化的聚類算法。 |
| compute_full_tree | ‘auto’ or bool, default=’auto’ 提前停止n_clusters樹的構建。如果聚類的數量與樣本數相比并不少,這對于減少計算時間是非常有用的。此選項僅在指定連接矩陣時才有用。還請注意,當改變聚類數量并使用緩存時,計算所有樹可能更有利。如果 distance_threshold是None, 它必須是True。通過默認的compute_full_tree設置是“auto”, 當distance_threshold不是None的時候就等價于True,或者n_clusters的最大值在100~0.02 * n_samples之間。否則,“auto”等同False。 |
| linkage | {“ward”, “complete”, “average”, “single”}, default=”ward” 使用哪種聯動標準。該算法將合并聚類,以最小化這一標準。 - Ward最小化會合并的聚類的差異。 - 平均使用兩組每次觀測的平均距離。 - 完全或最大連接使用兩個集合的所有觀測值之間的最大距離。 - 單次使用兩組所有觀測值之間的最小距離。 |
| distance_threshold | float, default=None 連接距離閾值高于該閾值,聚類將不會合并。如果不是None,則 n_clusters必須為None,并且compute_full_tree必須為True。 |
新版本0.21。
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| n_clusters_ | int 通過算法找到的聚類數。如果 distance_threshold=None=None,則它將等價于給定的n_clusters。 |
| labels_ | ndarray of shape (n_samples) 每一點的聚類標簽 |
| n_leaves_ | int 層次樹中的葉子節點數 |
| n_connected_components_ | int 圖中連通分量的估計數 新版本0.21中: n_connected_components_被添加以代替n_components_ |
| children_ | array-like of shape (n_samples-1, 2) 每個非葉節點的子節點。小于 n_samples的值對應于原始樣本樹的葉子。大于或等于n_samples的節點i是一個非葉節點,具有子節點children_[i - n_samples]。或者,在第i次迭代時,將children[i][0]和children[i][1]合并成節點n_samples + i。 |
示例
>>> from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
>>> import numpy as np
>>> X = np.array([[1, 2], [1, 4], [1, 0],
... [4, 2], [4, 4], [4, 0]])
>>> clustering = AgglomerativeClustering().fit(X)
>>> clustering
AgglomerativeClustering()
>>> clustering.labels_
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
fit(self, X[, y]) |
根據特征或距離矩陣進行層次聚類擬合 |
fit_predict(self, X[, y]) |
根據特征或距離矩陣擬合分層聚類,并返回聚類標簽。 |
get_params(self[, deep]) |
獲取此估計器的參數 |
set_params(self, **params) |
設置此估計器的參數 |
__init__(self, n_clusters=2, *, affinity='euclidean', memory=None, connectivity=None, compute_full_tree='auto', linkage='ward', distance_threshold=None)
初始化self。請參閱help(type(self))以獲得準確的說明。
fit(self, X, y=None)
根據特征或距離矩陣進行層次聚類擬合
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features) or (n_samples, n_samples) 要聚類的訓練實例,或實例之間的距離, 如果 affinity='precomputed' |
| y | Ignored 未使用,在此按約定呈現為API一致性。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| self | - |
fit_predict(self, X, y=None)
根據特征或距離矩陣進行層次聚類擬合
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features) or (n_samples, n_samples) 要聚類的訓練實例,或實例之間的距離, 如果 affinity='precomputed' |
| y | Ignored 未使用,在此按約定呈現為API一致性。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| labels | ndarray, shape (n_samples,) 聚類標簽 |
get_params(self, deep=True)
獲取此估計器的參數
| 表格 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| deep | bool, default=True 如果為True,則將返回此估計器的參數和所包含的作為估計量的子對象。 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| params | mapping of string to any 映射到其值的參數名稱 |
set_params(self, **params)
設置此估計器的參數
該方法適用于簡單估計器以及嵌套對象(例如pipelines)。后者具有表單的 <component>__<parameter>參數,這樣就可以更新嵌套對象的每個組件。
| 參數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估計器參數 |
| 返回值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估計器實例 |